Packages and Import
Package = directory. Java classes can be grouped together in packages. A package name is the same as the directory (folder) name which contains the .java files. You declare packages when you define your Java program, and you name the packages you want to use from other libraries in an import statement.
-
Package declaration The first statement, other than comments, in a Java source file, must be the package declaration.
Default package. Altho all Java classes are in a directory, it’s possible to omit the package declaration. For small programs it’s common to omit it, in which case Java creates what it calls a default package. Sun recommends that you do not use default packages.
-
Package declaration syntax 1.Package statment (optional). 2.Imports (optional). 3.Class or interface definitions.
// This source file must be Drawing.java in the illustration directory.
package illustration;
import java.awt.*;
public class Drawing { . . . }
Common imports
There are 166 packages containing 3279 classes and interfaces in Java 5. #### ex :
import java.awt.*; Common GUI elements.
import java.awt.event.*; The most common GUI event listeners.
import FAQ
Q: Is the order of the imports important?
A: No. Group them for readability.
Q: I've imported java.awt.*, why do I also need java.awt.event.*?
A: The wildcard "*" only makes the classes in this package visible, not any of the subpackages.
A Guide to Java Loops
Here are the types of loops that we can find in Java:
1.Simple for loop 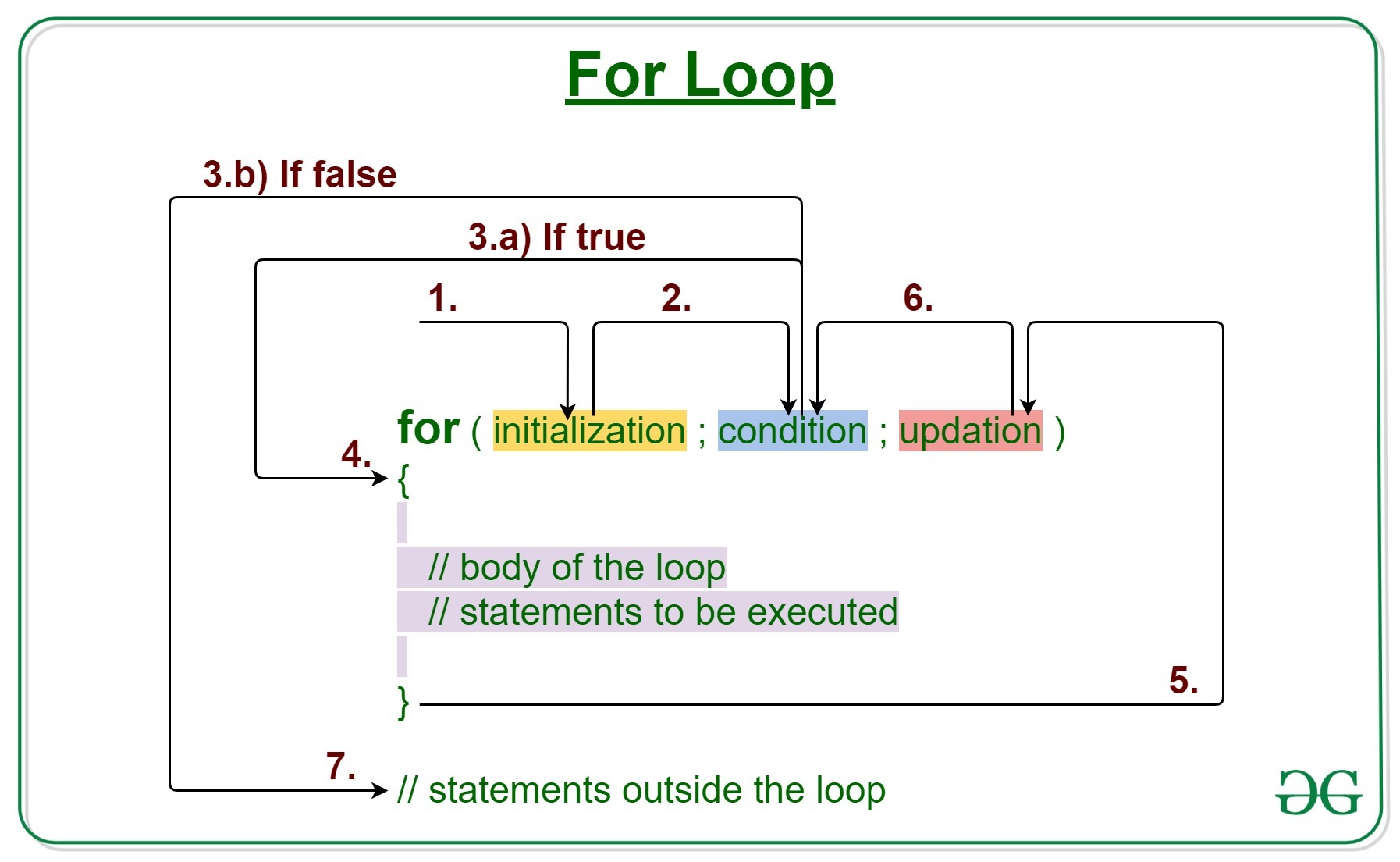
2.Enhanced for-each loop 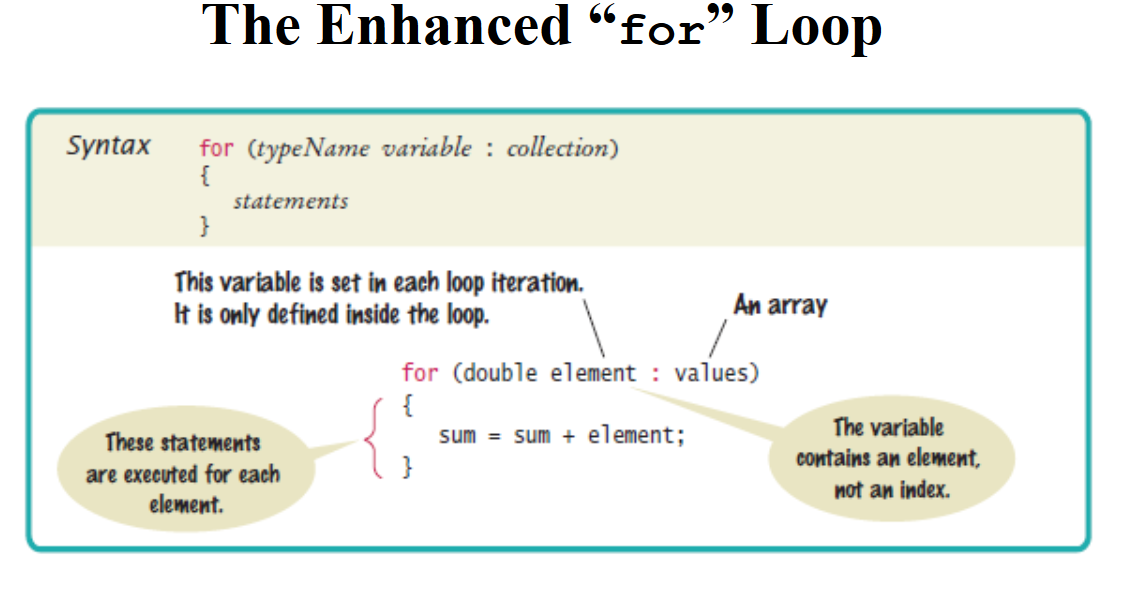
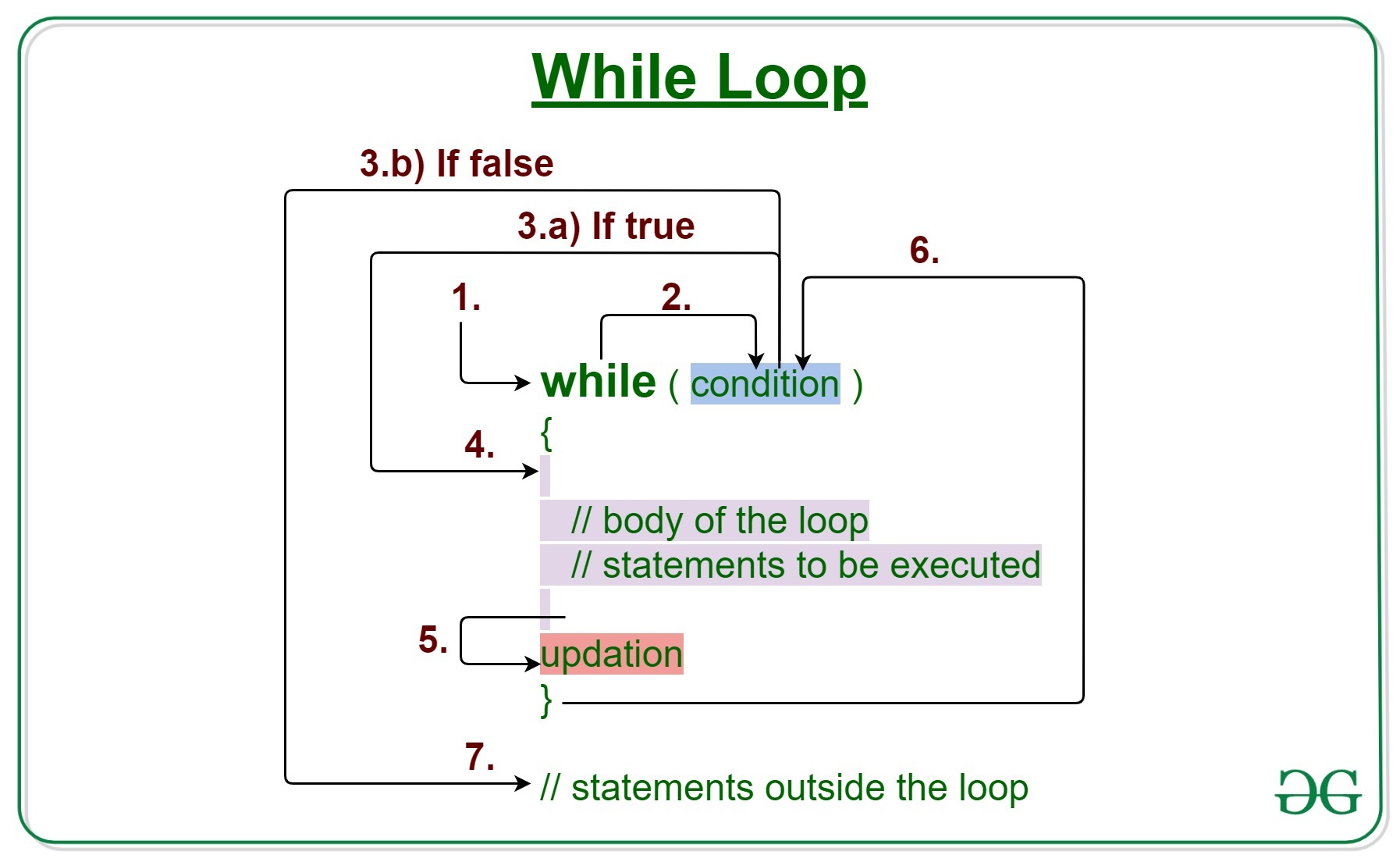
3.While loop
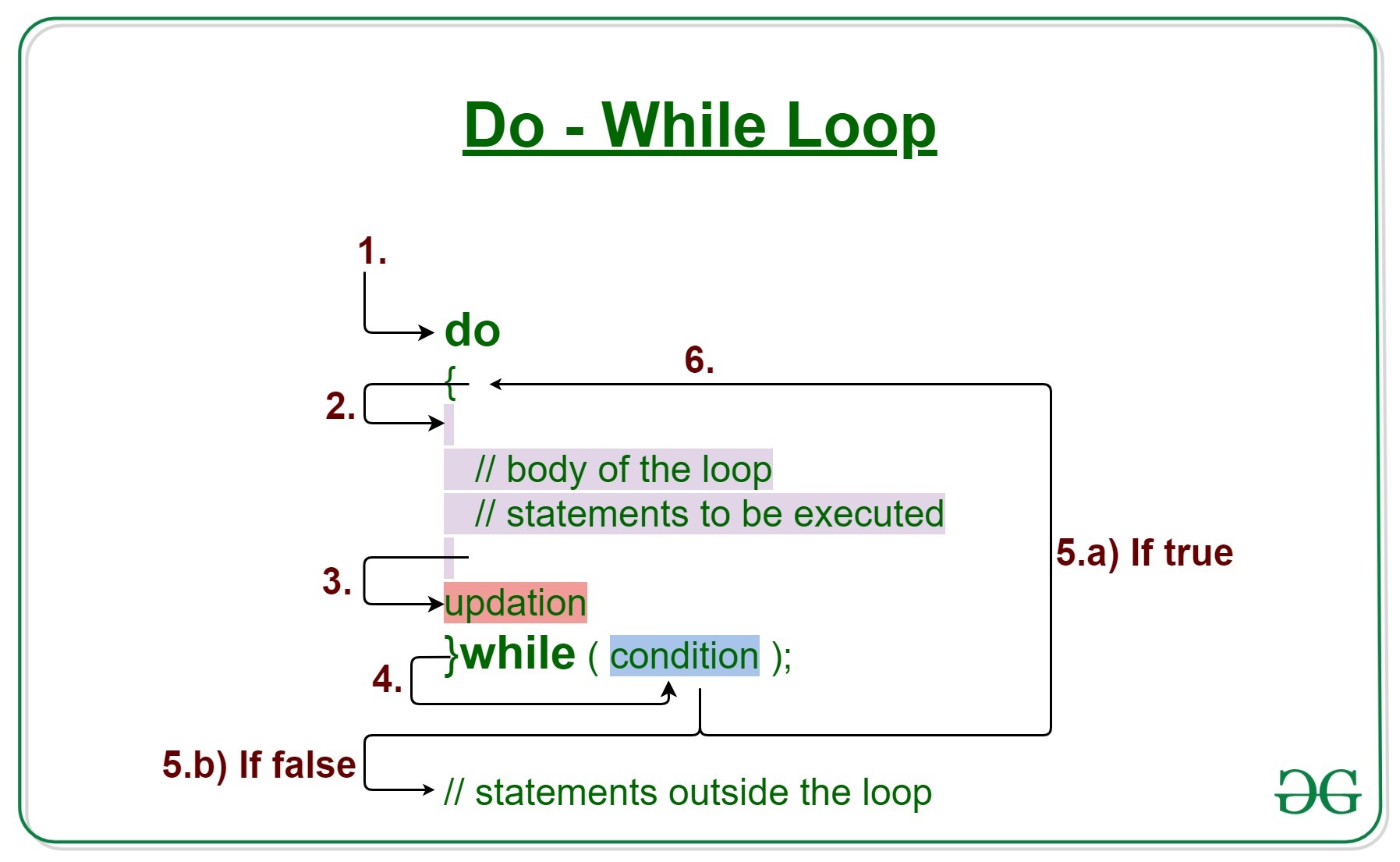
 4.Do-While loop
4.Do-While loop